
The advantages and the limitations of LC-MS/MS and Elisa methods in bioanalysis.
In biomolecular analysis, the pursuit of precision and accuracy drives the selection of analytical methodologies. Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) represent two contrasting approaches in this domain.
LC-MS/MS vs. ELISA: Accurate biomolecular measurements
In biomolecular analysis, the pursuit of precision and accuracy drives the selection of analytical methodologies. Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) represent two contrasting approaches in this domain. Understanding the nuanced advantages of each method is fundamental to unveiling their distinct capabilities and implications in the field of analytical science.
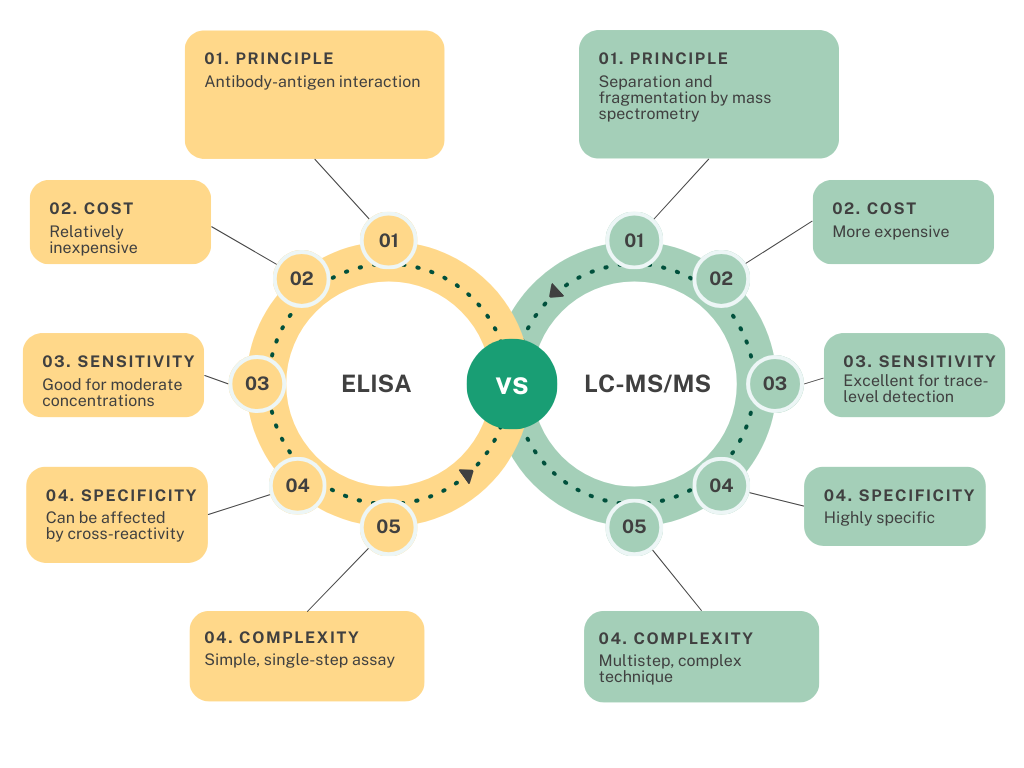
| Feature | ELISA | LC-MS/MS |
|---|---|---|
| Principle | Antibody-antigen interaction | Separation and fragmentation by mass spectrometry |
| Complexity | Simple, single-step assay | Multistep, complex technique |
| Cost-effectiveness | Relatively inexpensive | More expensive |
| Sensitivity | Good for moderate concentrations | Excellent for trace-level detection |
| Specificity | Can be affected by cross-reactivity | Highly specific |
| Applications | Clinical diagnostics, drug development, research | Clinical diagnostics, drug development, research, environmental monitoring, forensic analysis |
ELISA : A time-tested method with limitations
ELISA has been a mainstay in biomolecular analysis for decades, favored for its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and versatility. This technique is based on the interaction between antigens and antibodies and is used to detect and measure specific biomolecules, which is essential for disease diagnostics, drug development, and research. Particularly notable is ELISA’s application in clinical settings, where it is employed to detect and quantify biomarkers associated with a range of diseases, including cancer, inflammation, and cardiovascular disorders.
However, ELISA harbors inherent limitations. The technique’s reliance on antibodies introduces vulnerabilities like batch-to-batch variability, cross-reactivity, and a blind spot for specific protein isoforms or modifications. These drawbacks can impede accuracy, particularly in complex biological matrices, where subtle differences between closely related molecules hold the key to unlocking critical insights. As a result, ELISA-derived data can unintentionally bias our understanding of biological processes, leading to research conclusions built on shaky foundations. This can hinder drug development, impede the search for disease biomarkers, and ultimately hinder progress in biomedical research.
LC-MS/MS : Precision, sensitivity, and specificity in biomolecular analysis
While ELISA has long served as a mainstay in biomolecular analysis, LC-MS/MS has emerged as a gold standard, revolutionizing the field with its precision, sensitivity, and specificity. This method uses a combination of liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry to provide a comprehensive approach to identifying, quantifying, and characterizing biomolecules with unprecedented accuracy.
In contrast to ELISA’s reliance on antibodies, LC-MS/MS offers a direct, molecule-by-molecule analysis, enabling the identification, quantification, and even characterization of biomolecules with unparalleled accuracy. It excels in dissecting complex protein mixtures, pinpointing subtle post-translational modifications, and unraveling the intricate details often obscured by the limitations of traditional methods.
However, it’s crucial to acknowledge that LC-MS/MS is a sophisticated technique that demands specialized expertise and instrumentation, making it more costly and time-consuming than simpler methods like ELISA. Additionally, the complexity of LC-MS/MS analyses may require specialized software and expertise for data interpretation.
Despite these considerations, LC-MS/MS remains the gold standard for demanding biomolecular analysis applications, where the highest levels of precision, sensitivity, and specificity are paramount. Its contributions to various fields, including drug discovery, biomarker identification, and clinical diagnostics, are undeniable.
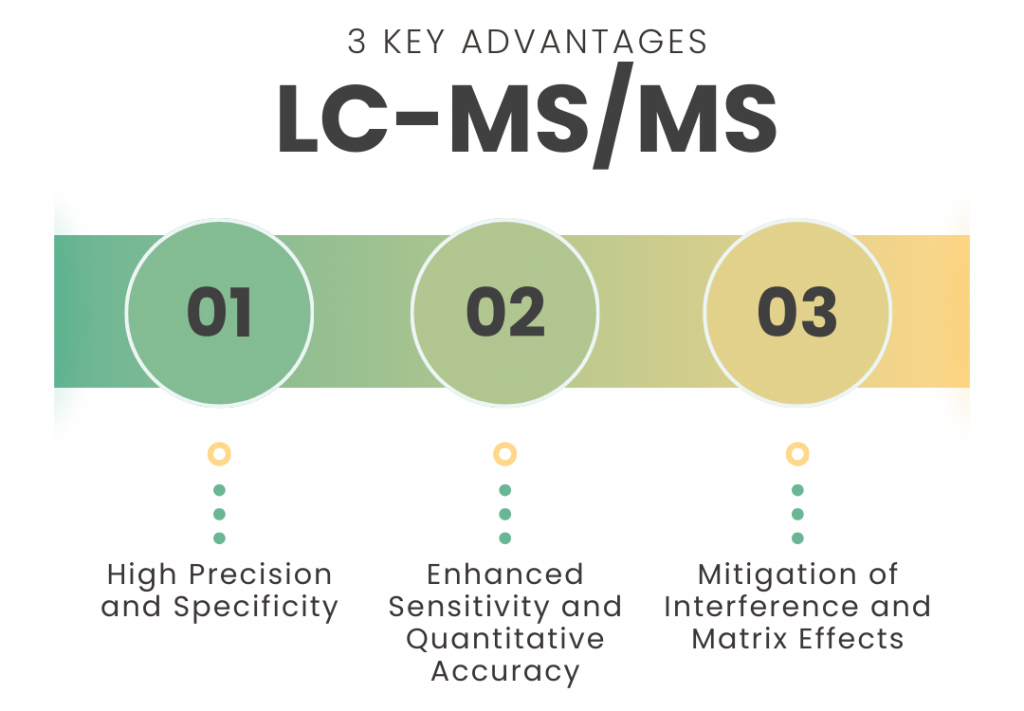
The key advantages of LC-MS/MS over ELISA:
- High Precision and Specificity: LC-MS/MS’s ability to differentiate between molecular isoforms, modifications, and structurally similar compounds far exceeds the capabilities of ELISA. This precision is invaluable in pharmaceutical research, clinical diagnostics, and biomarker discovery.
- Enhanced Sensitivity and Quantitative Accuracy: LC-MS/MS’s superior sensitivity allows for the detection and quantification of molecules at significantly lower concentrations compared to ELISA. Its wide dynamic range ensures accurate measurements across diverse sample matrices, enabling precise drug concentration analysis and biomarker detection.
- Mitigation of Interference and Matrix Effects: LC-MS/MS minimizes issues related to matrix effects and interference; common hurdles encountered in ELISA. This advantage ensures more robust and reproducible results, even in complex biological samples.
Biotrial’s distinct expertise in LC-MS/MS
Biotrial stands as an industry leader in LC-MS/MS, a sophisticated analytical technique that requires a high level of expertise compared to simpler methods like ELISA. This expertise enables Biotrial to excel in three key areas:
- Precision Medicine and Drug Development: Biotrial’s proficiency in LC-MS/MS allows for precise quantification of drug concentrations in clinical trials, facilitating pharmacokinetic assessments critical for drug development and dosage determination.
- Advanced Biomarker Discovery: Leveraging LC-MS/MS, Biotrial identifies and validates biomarkers with exceptional sensitivity and accuracy. This capability contributes significantly to early disease detection and personalized treatment approaches.
- Cutting-Edge Method Development: Biotrial’s commitment to innovation and method development ensures the creation and validation of robust LC-MS/MS methodologies. These methodologies comply with stringent regulatory standards, ensuring reliability in data crucial for regulatory submissions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ELISA and LC-MS/MS are two distinct analytical techniques with unique strengths and limitations. ELISA, while relatively simple and cost-effective, is inherently less precise and specific than LC-MS/MS. LC-MS/MS, on the other hand, offers unparalleled precision, sensitivity, and specificity, making it the gold standard for demanding biomolecular analysis applications. Biotrial, with its expertise in LC-MS/MS, excels in areas such as precision medicine, biomarker discovery, and method development.

