PK studies
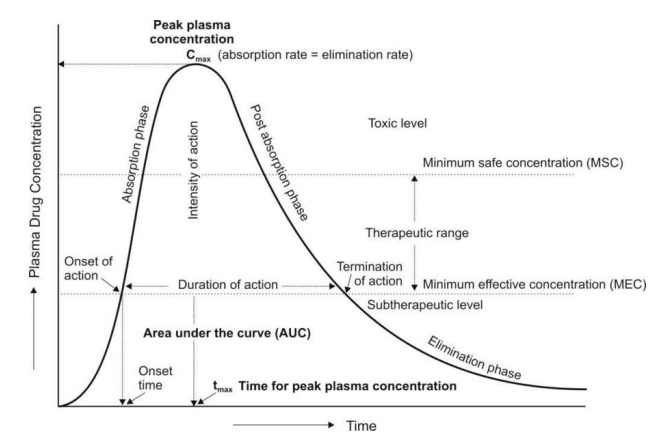
Pharmacokinetic (PK) studies are an essential part of preclinical research. They provide information on how a drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted in the body. This information is critical for understanding the safety and efficacy of a drug, and for designing clinical trials.
Here are some of the key benefits of PK studies in preclinical research:
- Identify safety risks. PK studies can help to identify potential safety risks associated with a drug, such as toxicity or drug-drug interactions. This information can be used to inform the design of clinical trials and to mitigate safety risks.
- Determine optimal dosing. PK studies can help to determine the optimal dosing regimen for a drug, including the dose level, frequency of administration, and route of administration. This information is essential for ensuring that patients receive the correct dose of the drug to achieve the desired therapeutic effect.
- Predict human PK. PK studies in animals can be used to predict how a drug will behave in humans. This information can be used to design clinical trials and to interpret clinical data.